
Sunscreen Myths Debunked: Protecting Your Skin Year-Round
Although sunscreen is widely recognized as an essential part of protecting your skin beyond hydration, persistent myths about this skincare product either continue to mislead or discourage people from using it altogether.
Sun care products come in many forms, including tinted sunscreens, hybrid sunscreens, sunscreen sticks, and moisturizers with SPF. They're designed to help protect your skin from the sun's harmful rays.
Advertisement

A woman applying spray sunscreen at the beach | Source: Getty Images
Advertisement
While protecting your skin from UV rays is essential, a concerning social media movement led by anti-sunscreen influencers gained popularity in 2024, and became the vehicle for spreading misinformation about the product.
Many of the myths perpetuated still persist today. Below, we debunk six of the most common misconceptions with expert insights.

A woman applying sunscreen in a sun shape on her back | Source: Getty Images
Advertisement
6 Common Myths About Sun Exposure and Sunscreen
Myth 1: The Sun Doesn't Cause Cancer
There's plenty of proof that too much sun exposure increases the risk of skin cancer. Dr. Dino Prato, founder and CEO of Envita Medical Centers, explains that ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun damage the DNA in skin cells, leading to mutations that can cause cancer.
"UV exposure wreaks havoc on the skin by generating free radicals that produce inflammation and damage your skin's DNA," Dr. Prato told Healthline.
Advertisement

A woman treating sunburn | Source: Getty Images
Advertisement
Dr. Susan Massick, a dermatologist at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, adds that excessive sun exposure can damage cells beyond repair. "It's these mutated cells that survive but can then turn precancerous and eventually cancerous in some cases," she says.
According to the Skin Cancer Foundation, about 90 percent of nonmelanoma skin cancers and 86 percent of melanomas are caused by solar UV rays. Even indoor tanning, which uses UV light, contributes to over 419,000 new skin cancer cases in the U.S. each year.
Advertisement

A woman in a tanning bed | Source: Getty Images
Advertisement
Myth 2: Sunscreen Is Bad for You
Dermatologists agree that sunscreen is safe and essential for healthy skin. "Numerous research studies have shown that wearing sunscreen minimizes both short- and long-term damage from the sun's rays," says Dr. Nkem Ugonabo, a board-certified dermatologist and CeraVe consultant.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) also regulates sunscreens to ensure they meet strict safety and effectiveness standards.
Advertisement
A dollop of sunscreen on skin | Source: Getty Images
Advertisement
Myth 3: Darker Skin Tones Don't Need Sun Protection
People with darker skin may be less likely to burn quickly, but they're still at risk for sun damage. "As a dermatologist, I recommend that everyone — regardless of skin type, tone, or texture — wear sunscreen every day, year-round," says Dr. Ugonabo. All skin tones can experience damage that leads to cancer, premature aging, and dark spots.

A young woman applying sunscreen on her friend's back | Source: Getty Images
Advertisement
Myth 4: You Don't Need Sunscreen Indoors, in the Shade, or While Driving
"The sun's rays aren't only a concern when you're outside," says Dr. Ugonabo. UVA rays can penetrate through glass and reflect off surfaces, meaning you can still be exposed indoors or in the shade. She advises applying (and reapplying) sunscreen daily, even when you plan to stay inside.

A woman applying sunscreen inside her home | Source: Getty Images
Advertisement
Myth 5: Sunscreen Doesn't Expire
It does. According to the FDA, all sunscreens must include an expiration date or remain effective for at least three years. Dermatologists recommend discarding expired products and storing sunscreen away from heat or direct sunlight, which can make it less effective.
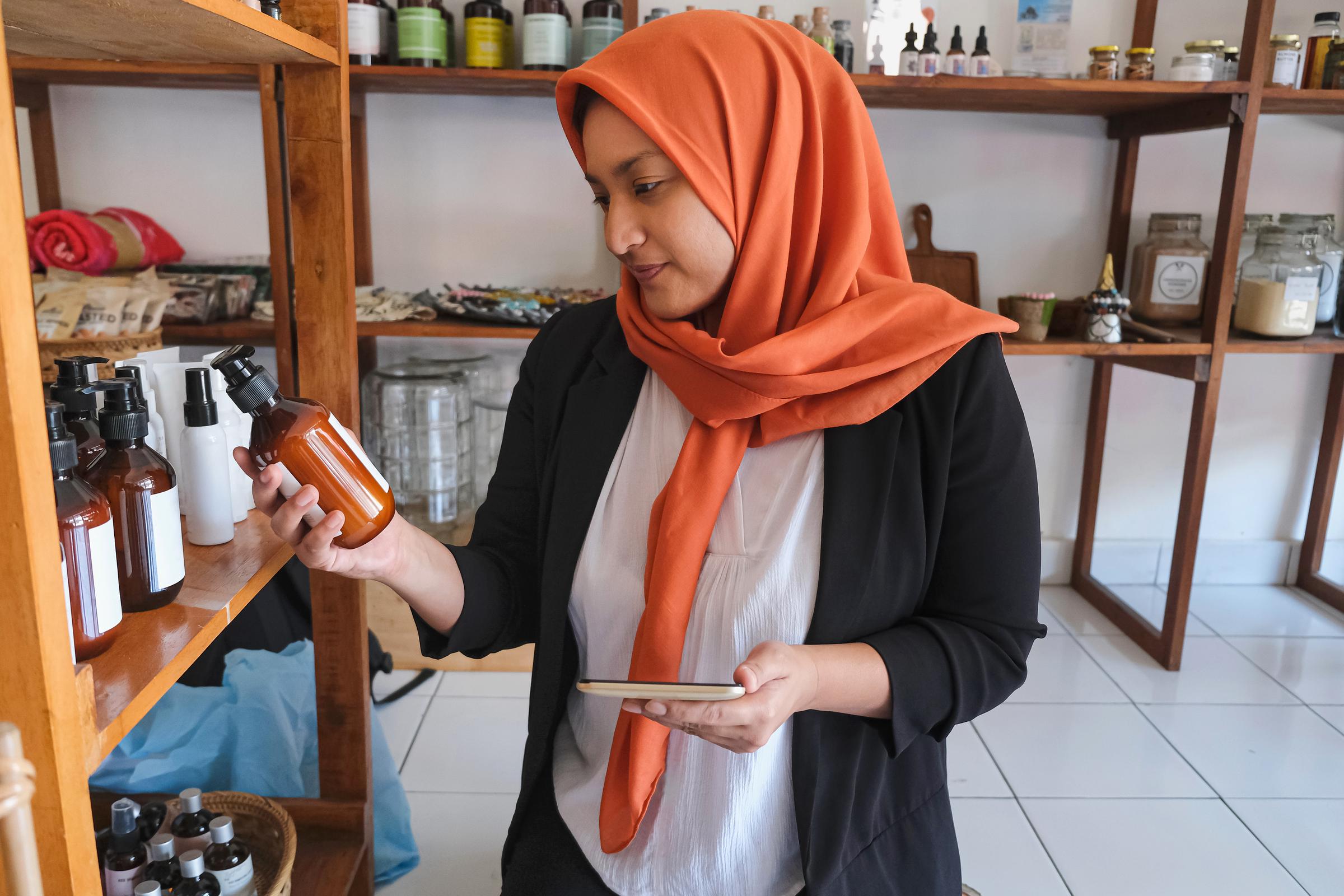

A woman checking the expiry date of a skincare product | Source: Getty Images
Advertisement
Myth 6: You Don't Need Sunscreen in the Winter or If It's Cloudy Outside
Its a common misconception that sunscreen isn't necessary when it's cloudy or cold. In reality, harmful UV rays are still present, even during winter or on overcast days.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), snow can reflect up to 80% of UV radiation. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also reports that UV rays can pass through up to 80% of light cloud cover.
Advertisement
"It's important to wear SPF all year round, during both the summer and winter months," says Dr. Ugonabo. "I remind my patients that UV rays are present on cloudy days as well. Just because you can't see the sun doesn't mean it can't see you." In other words, sunscreen should be part of your daily routine — not just when it's obviously sunny.
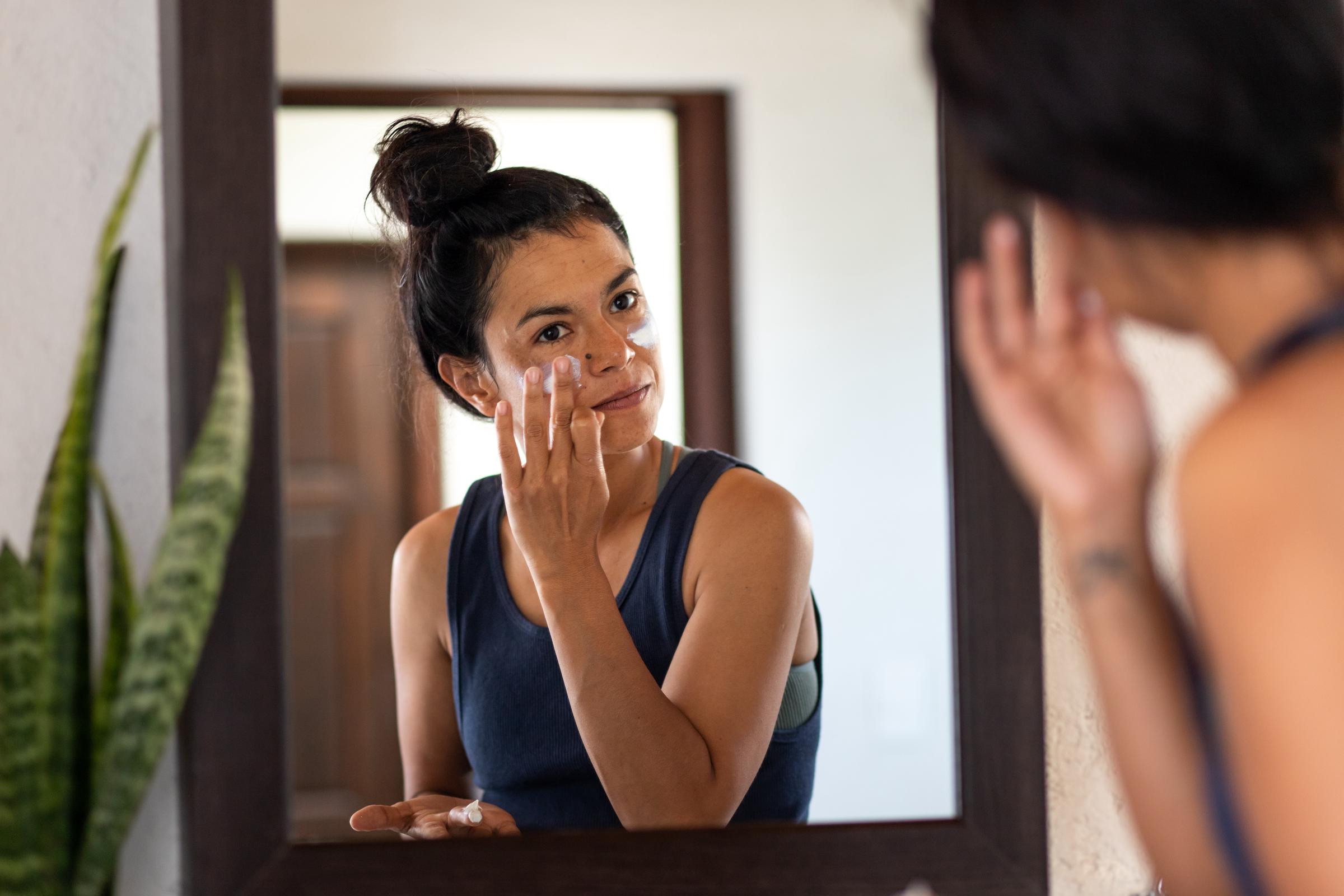

A woman applying sunblock to her face | Source: Getty Images
Sunscreen isn't just for sunny days or beach trips — it's a daily essential for long-term skin health. By protecting your skin from harmful UV rays, you're not only preventing sunburn but also reducing your risk of premature aging and skin cancer.
Advertisement
The information in this article is not intended or implied to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. All content, including text, and images contained on amoMedia.com, or available through amoMedia.com is for general information purposes only. amoMedia.com does not take responsibility for any action taken as a result of reading this article. Before undertaking any course of treatment please consult with your healthcare provider.
